Manual Testing Course-Day 16
What is Agile Testing?
AGILE TESTING is a testing practice that follows the rules and principles of agile software development. Unlike the Waterfall method, Agile Testing can begin at the start of the project with continuous integration between development and testing. Agile Testing methodology is not sequential (in the sense it's executed only after coding phase) but continuous.
Agile Test Plan
Agile test plan includes types of testing done in that iteration like test data requirements, infrastructure, test environments, and test results. Unlike the waterfall model, in an agile model, a test plan is written and updated for every release. Typical test plans in agile includes
- Testing Scope
- New functionalities which are being tested
- Level or Types of testing based on the features complexity
- Load and Performance Testing
- Infrastructure Consideration
- Mitigation or Risks Plan
- Resourcing
- Deliverables and Milestones
Agile Testing Strategies
Agile testing life cycle spans through four stages
(a) Iteration 0
During the first stage or iteration 0, you perform initial setup tasks. It includes identifying people for testing, installing testing tools, scheduling resources (usability testing lab), etc. The following steps are set to achieve in Iteration 0
a) Establishing a business case for the project
b) Establish the boundary conditions and the project scope
c) Outline the key requirements and use cases that will drive the design trade-offs
d) Outline one or more candidate architectures
e) Identifying the risk
f) Cost estimation and prepare a preliminary project
(b) Construction Iterations
The second phase of agile testing methodology is Construction Iterations, the majority of the testing occurs during this phase. This phase is observed as a set of iterations to build an increment of the solution. In order to do that, within each iteration, the team implements a hybrid of practices from XP, Scrum, Agile modeling, and agile data and so on.
In construction iteration, the agile team follows the prioritized requirement practice: With each iteration, they take the most essential requirements remaining from the work item stack and implement them.
Construction iteration is classified into two, confirmatory testing and investigative testing. Confirmatory testing concentrates on verifying that the system fulfills the intent of the stakeholders as described to the team to date, and is performed by the team. While the investigative testing detects the problem that confirmatory team has skipped or ignored. In Investigative testing, tester determines the potential problems in the form of defect stories. Investigative testing deals with common issues like integration testing, load/stress testing, and security testing.
Again for, confirmatory testing there are two aspects developer testing and agile acceptance testing. Both of them are automated to enable continuous regression testing throughout the lifecycle. Confirmatory testing is the agile equivalent of testing to the specification.
Agile acceptance testing is a combination of traditional functional testing and traditional acceptance testing as the development team, and stakeholders are doing it together. While developer testing is a mix of traditional unit testing and traditional service integration testing. Developer testing verifies both the application code and the database schema.
(c) Release End Game Or Transition Phase
The goal of “Release, End Game” is to deploy your system successfully into production. The activities include in this phase are training of end users, support people and operational people. Also, it includes marketing of the product release, back-up & restoration, finalization of system and user documentation.
The final agile methodology testing stage includes full system testing and acceptance testing. In accordance to finish your final testing stage without any obstacles, you should have to test the product more rigorously while it is in construction iterations. During the end game, testers will be working on its defect stories.
(d) Production
After the release stage, the product will move to the production stage.
The Agile Testing Quadrants
The agile testing quadrants separate the whole process in four Quadrants and help to understand how agile testing is performed.
a) Agile Quadrant I – The internal code quality is the main focus in this quadrant, and it consists of test cases which are technology driven and are implemented to support the team, it includes
1. Unit Tests
2.Component Tests
b) Agile Quadrant II – It contains test cases that are business driven and are implemented to support the team. This Quadrant focuses on the requirements. The kind of test performed in this phase is
1. Testing of examples of possible scenarios and workflows
2. Testing of User experience such as prototypes
3. Pair testing
c) Agile Quadrant III – This quadrant provides feedback to quadrants one and two. The test cases can be used as the basis to perform automation testing. In this quadrant, many rounds of iteration reviews are carried out which builds confidence in the product. The kind of testing done in this quadrant is
1. Usability Testing
2. Exploratory Testing
3. Pair testing with customers
4. Collaborative testing
5. User acceptance testing
d) Agile Quadrant IV – This quadrant concentrates on the non-functional requirements such as performance, security, stability, etc. With the help of this quadrant, the application is made to deliver the non-functional qualities and expected value.
1. Non-functional tests such as stress and performance testing
2. Security testing with respect to authentication and hacking
3. Infrastructure testing
4. Data migration testing
5. Scalability testing
QA challenges with agile software development
a) Chances of error are more in agile, as documentation is given less priority, eventually puts more pressure on QA team
b) New features are introduced quickly, which reduces the available time for test teams to identify whether the latest features are according to the requirement and does it truly address the business suits
c) Testers are often required to play a semi-developer roled
d) Test execution cycles are highly compressed
e) Very less time to prepare test plan
f) For regression testing, they will have minimal timing
g) Change in their role from being a gate-keeper of quality to being a partner in Quality
h) Requirement changes and updates are inherent in an agile method, becoming the biggest challenge for QA
Risk of Automation in Agile Process
- Automated UI provides a high level of confidence, but they are slow to execute, fragile to maintain and expensive to build. Automation may not significantly improve test productivity unless the testers know how to test
- Unreliable tests are a major concern in automated testing. Fixing failing tests and resolving issues related to brittle tests should be a top priority in order to avoid false positives
- If the automated test are initiated manually rather than through CI (Continuous Integration) then there is a risk that they are not regularly running and therefore may cause failing of tests
- Automated tests are not a replacement for an exploratory manual testing. To obtain the expected quality of the product, a mixture of testing types and levels is required
- Many commercially available automation tools provide simple features like automating the capture and replay of manual test cases. Such tool encourages testing through the UI and leads to an inherently brittle and difficult to maintain tests. Also, storing test cases outside the version control system creates unnecessary complexity
- In order to save time, much times the automation test plan is poorly planned or unplanned which results in the test fail
- A test set up and tear down procedures are usually missed out during test automation, while Performing manual testing, a test set up and tear down procedures sounds seamless
- Productivity metrics such as a number of test cases created or executed per day can be terribly misleading, and could lead to making a large investment in running useless tests
- Members of the agile automation team must be effective consultants: approachable, cooperative, and resourceful, or this system will quickly fail
- Automation may propose and deliver testing solutions that require too much ongoing maintenance relative to the value provided
- Automated testing may lack the expertise to conceive and deliver effective solutions
- Automated testing may be so successful that they run out of important problems to solve, and thus turn to unimportant problems.
Conclusion
Agile methodology in software testing involves testing as early as possible in the software development lifecycle. It demands high customer involvement and testing code as soon as it becomes available. The code should be stable enough to take it to system testing. Extensive regression testing can be done to make sure that the bugs are fixed and tested. Mainly, Communication between the teams makes agile model testing success!!!
Mutation Testing
Mutation Testing is a type of software testing in which certain statements of the source code are changed/mutated to check if the test cases are able to find errors in source code. The goal of Mutation Testing is ensuring the quality of test cases in terms of robustness that it should fail the mutated source code.
The changes made in the mutant program should be kept extremely small that it does not affect the overall objective of the program. Mutation Testing is also called Fault-based testing strategy as it involves creating a fault in the program and it is a type of White Box Testing which is mainly used for Unit Testing.
Mutation was originally proposed in 1971 but lost fervor due to the high costs involved. Now, again it has picked steam and is widely used for languages such as Java and XML.
How to execute Mutation Testing?
Following are the steps to execute mutation testing(mutation analysis):
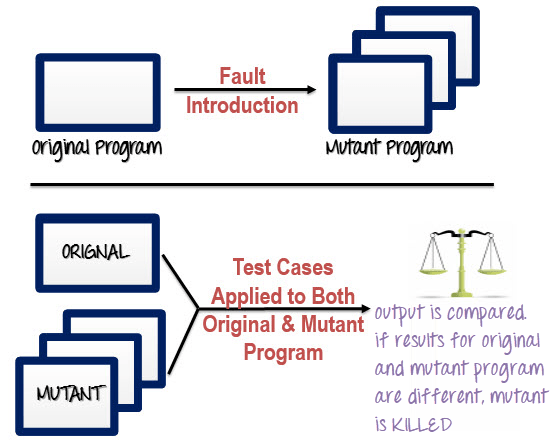
Step 1: Faults are introduced into the source code of the program by creating many versions called mutants. Each mutant should contain a single fault, and the goal is to cause the mutant version to fail which demonstrates the effectiveness of the test cases.
Step 2: Test cases are applied to the original program and also to the mutant program. A Test Case should be adequate, and it is tweaked to detect faults in a program.
Step 3: Compare the results of an original and mutant program.
Step 4: If the original program and mutant programs generate the different output, then that the mutant is killed by the test case. Hence the test case is good enough to detect the change between the original and the mutant program.
Step 5: If the original program and mutant program generate the same output, Mutant is kept alive. In such cases, more effective test cases need to be created that kill all mutants.
How to Create Mutant Programs?
A mutation is nothing but a single syntactic change that is made to the program statement. Each mutant program should differ from the original program by one mutation.
| Original Program | Mutant Program |
|---|---|
| If (x>y) Print "Hello" Else Print "Hi" | If(x<y) Print "Hello" Else Print "Hi" |
What to change in a Mutant Program?
There are several techniques that could be used to generate mutant programs. Let's look at them
| Operand replacement operators | Expression Modification Operators | Statement modification Operators |
|---|---|---|
| Replace the operand with another operand (x with y or y with x) or with the constant value. | Replace an operator or insertion of new operators in a program statement. | Programmatic statements are modified to create mutant programs. |
| Example- If(x>y) replace x and y values If(5>y) replace x by constant 5 | Example- If(x==y) We can replace == into >= and have mutant program as If(x>=y) and inserting ++ in the statement If(x==++y) | Example- Delete the else part in an if-else statement Delete the entire if-else statement to check how a program behaves Some of sample mutation operators:
|
Automation of Mutation Testing:
Mutation testing is extremely time consuming and complicated to execute manually. To speed up the process, it is advisable to go for automation tools. Automation tools reduce the cost of testing as well.
List of tools available -
- Stryker
- PIT Testing
Types of Mutation Testing
In Software Engineering, Mutation testing could be fundamentally categorized into 3 types– statement mutation, decision mutation, and value mutation.
- Statement Mutation - developer cut and pastes a part of a code of which the outcome may be a removal of some lines
- Value Mutation- values of primary parameters are modified
- Decision Mutation- control statements are to be changed
Mutation Score:
The mutation score is defined as the percentage of killed mutants with the total number of mutants.
- Mutation Score = (Killed Mutants / Total number of Mutants) * 100
Test cases are mutation adequate if the score is 100%. Experimental results have shown that mutation testing is an effective approach for measuring the adequacy of the test cases. But, the main drawback is that the high cost of generating the mutants and executing each test case against that mutant program.
Advantages of Mutation Testing:
Following are the advantages of Mutation Testing:
- It is a powerful approach to attain high coverage of the source program.
- This testing is capable comprehensively testing the mutant program.
- Mutation testing brings a good level of error detection to the software developer.
- This method uncovers ambiguities in the source code and has the capacity to detect all the faults in the program.
- Customers are benefited from this testing by getting a most reliable and stable system.
Disadvantages of Mutation Testing:
On the other side, the following are the disadvantages of Mutant testing:
- Mutation testing is extremely costly and time-consuming since there are many mutant programs that need to be generated.
- Since its time consuming, it's fair to say that this testing cannot be done without an automation tool.
- Each mutation will have the same number of test cases than that of the original program. So, a large number of mutant programs may need to be tested against the original test suite.
- As this method involves source code changes, it is not at all applicable for Black Box Testing.
Conclusion:
Do you want exhaustive testing of your application? The answer is Mutation testing. It is the most comprehensive technique to test a program. This is the method which checks for the effectiveness and accuracy of a testing program to detect the faults or errors in the system.




Comments
Post a Comment