Manual Testing Course-Day 16
ETL (Extraction, Transformation and Loading) Testing
ETL testing is done before data is moved to production data warehouse systems. It is also called as table balancing or product reconciliation. ETL testing is different from Database testing in terms of its scope and the steps followed during this testing.
ETL testing is to ensure that the data which has been loaded from a source to destination after transformation is accurate. It involves the verification of data at various stages, which is used between source and destination.
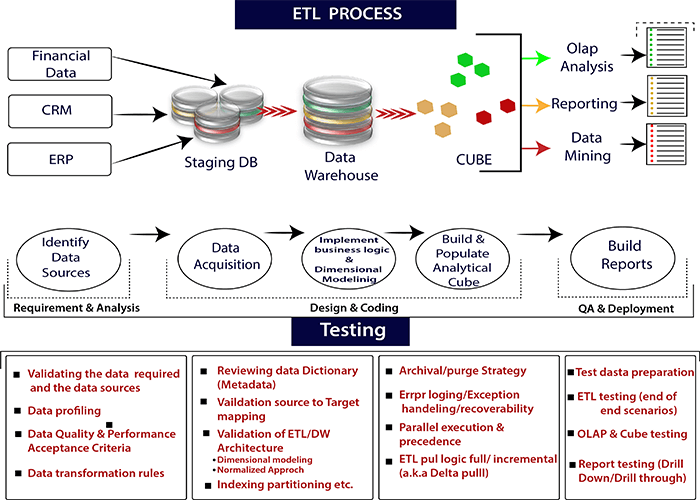
Process for ETL testing
Like other testing process, ETL testing also go through some testing processes.
ETL testing performed in five stages.
- ETL testing identifies data sources and requirements.
- Data recovery
- Implement dimensional modeling and business logic.
- Build and populate data
- Build reports
Types of ETL testing
The types of ETL testing are:
1. New Data Warehouse Testing: It is built and verified from the core. In this testing, the input is taken from the customer's requirement and different data sources. However, the new data warehouse is built and verified with the help of ETL tools.
Here are the responsibilities which are played by different groups:
- Business Analyst: Business Analyst gathers and documents the requirements.
- Infrastructure People: These people set up the test environment.
- QA Testers: QA Testers develop test plans and test scripts and then execute these test plan and scripts.
- Developers: Developers perform the unit test for each module.
- Database Administrator: Database Administrator test for the performance and also for the stress.
- Users: Users do functional testing, which includes UAT (User Acceptance Testing).
2. Production Validation Testing: This testing is done on data when data is moved to production systems. Informatica Data Validation option provides the automation of ETL testing and management capabilities to ensure that the data do not compromise production systems.
3. Source to Target Testing (Validation): This type of testing is done to validate the data values transformed the expected data values.
4. Application Upgrade: This type of ETL testing is automatically generated, which saves the test development time. This type of testing checks the extracted data from an older application are precisely same as the data in a new application.
5. Metadata Testing: Metadata testing includes the measurement of types of data, length of data, and check index/constraint.
6. Data Accuracy Testing: This testing is done to ensure that the data is accurately loaded and transformed as expected.
7. Data Transformation Testing: Data transformation testing done in many cases. It cannot be achieved by writing one source SQL query and comparing the output with the target. Multiple SQL queries need to be run for each row to verify the transformation rules.
8. Data Quality Testing: Data Quality Tests includes syntax and reference test. To avoid any error due to date or order number during business process data quality is done. Syntax tests: It will report dirty data, based on invalid character, character pattern, incorrect upper or lower case order, etc. Reference Tests: It will check the data according to the data model.
For Example, Customer ID data quality testing includes number check, date check, precision check, date check, etc.
9. Incremental ETL Testing: This testing is done to check the data integrity of old and new data when the new data added. Incremental testing verifies that the system processes correctly even after the insertion and updating the data during an incremental ETL process.
10. GUI/Navigation Testing: This testing is done to check the navigation or GUI aspects of the front end reports.
11. Migration Testing: In this testing, the customer has an existing data warehouse, and ETL is performing the job. But customers are looking for tools to improve efficiency. It includes these steps:
- Design and validation tests
- Setting up the test environment
- Executing the validation test
- Reporting the bugs
12. Change Requests: In this case, data added to an existing data warehouse. There might be condition arises where customers require to change the present business rule, or they can integrate new rule.
13. Report Testing: The final result of the data warehouse, reported testing. Repots should test by validating the data, layout in the report. Reports are an essential resource for creating vital business decisions.
Tasks performed in ETL Testing
Tasks involved in ETL testing are:
- Understanding of data, used for reporting
- Data Model Reviewing
- Mapping of the source to target
- Checks the data in the source data
- Validation of packages and schema
- In the target system, data verification should be done
- Verification of aggregation rules and data transformation calculation
- Data comparison between the target system and data source
- For the target system, quality and data integrity should be examined.
- Performance testing of data.
Differences between the ETL and the Database Testing
ETL and database testing involve data validation, but both are not same. ETL testing is usually performed on data in a data warehouse, whereas, database testing is performed on transactional systems. Data comes into the transactional database from different applications.
Operations performed in ETL Testing
ETL testing involves the following operations:
- Validation of data movement from source to the target system.
- Data count verification in the source and target system.
- ETL testing verifies the transformation, extraction as per requirement and expectation.
- ETL testing verifies if table relations join and keys are preservers during the transformation.
The operation performed in Database Testing
Database testing focuses on data accuracy, the correctness of data, and valid values.
Database testing performs the following operations:
- Database testing focuses on verification of the column in a table that has valid data values.
- To verify whether the primary or foreign key is maintained, database testing is used.
- Database testing verifies if the data is missing in the column. Here, we check that are there any null values in columns which should have a valid value?
- We verify the accuracy of data in columns.
For example, the Number of month's column shouldn't have a value greater than 12.
| Function | ETL Testing | Database Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | ETL testing is performed for data extraction, transformation and loading for BI reporting. | Database testing is performed to validate and integrate the data. |
| Business Need | ETL testing used for information, forecasting, and analytical reporting. | This testing is used to integrate the data from multiple applications and server impact. |
| Applicable System | ETL testing contains historic data that cannot be used in business flow environment. | ETL testing contains the transactional system where the flow of business occurs. |
| Modeling | The multidimensional method is used. | ER method is used. |
| Database Type | ETL testing is applied to OLAP systems. | Database testing is used in OLTP system. |
| Data Type | ETL uses the de-normalized data with fewer joins, more indexes, and aggregations. | The database uses normalized data with joins. |
| Common Tools | QuerySurge, Informatica, etc. tools are used. | QTP, Selenium tools are used in database testing. |
ETL performance Testing
ETL performance testing is used to ensure if an ETL system can handle an expected load of multiple users and transactions. Performance testing involves server-side workload on the ETL system.
How to perform ETL testing performance?
Here are the following steps which are followed to test the performance of ETL testing:
Step 1: Find the load which transformed in production.
Step 2: New data will be created of the same load or move it from production data to a local server.
Step 3: Now, we will disable the ETL until the required code is generated.
Step 4: We will count the needed data from the database table.
Step 5: We will note down the last run of ETL and enable the ETL. It will get enough stress to transform the entire load which has created and run it.
Step 6: After the completion of ETL, we will count the created data.
Essential performance that should be noted:
- Find out the total time taken to transform the load
- Find out the performance that has been improved or dropped.
- We will check if the entire expected load is extracted and transferred.
Data Accuracy in ETL Testing
In ETL Testing, we focus on data accuracy to ensure whether the data is accurately loaded to the target system as per our expectations.
Here are the steps which should be followed to perform the data accuracy are:
Value Comparison: In value comparison, we compare the data in the source and target system with minimum or no transformation. ETL testing can be possible by using various ETL tools. For example, Source Qualifier Transformation in Informatica.
Expression Transformation can also be performed in data accuracy testing. Set of operators can be used in SQL statements to check the data accuracy in the source and the target systems.
Check the columns of critical data: Critical Data columns can be checked by comparing the distinct values in the source and the target system.
ETL testing in data transformation
It is quite complex to perform the data transformation because it cannot be achieved by writing a single SQL query and comparing the output with the target. To do the ETL testing for Data Transformation, we have to write multiple SQL queries for each row to verify the transformation rules.
To perform the successful ETL testing for data transformation, we have to pick the sufficient and sample data from the source system to apply the transformation rule.
The significant steps to perform ETL testing for data transformation are:
Step 1. The first step is to create a scenario for input data and the expected results. Now we will validate ETL testing with the business customer. ETL testing is the best approach to gather the requirements during designs and can be used as a part of testing.
Step 2. The second step is to create the test data according to the scenario. ETL developer will automate the entire process of populating the datasets with the scenario spreadsheet permit versatility and mobility for the reason that the situation is changed.
Step 3. Utilize the data profiling and the results will compare the range and submission of values in each field between the source and the target data.
Step 4. We will validate the accurate processing of ETL generated fields. For example, Surrogate keys.
Step 5. We will validate the data types within the warehouse that are the same as specified in the data model or design.
Step 6. Scenarios of data will be created between tables which test the referential integrity.
Step 7. We will validate the parent to child relationship in the data.
Step 8. And at the end, we will perform lookup transformation. Lookup query should be straight without any data gathering and expected to return only one value as per the source table. We can directly join the lookup table in the source qualifier. If this is not a case, we will write a query which will join the lookup table with the main table in the source and will compare the data in the corresponding column in the target.
ETL Test Cases
The objective of ETL testing is to assure that the loaded data from source to destination after business transformation is accurate.
ETL testing applies to different tools and databases in the information management industry.
During the ETL testing performance, two documents always used by the ETL tester which are:
1. ETL mapping sheets: ETL mapping sheets contain all the information of the source and destination tables, which includes every column and their lookup in the reference table. ETL tester needs to be comfortable with SQL queries as ETL testing may involve writing big queries with multiple joins to validate the data at any stage of ETL. ETL mapping sheets provide significant help when we write queries for data verification.
2. DB Schema of Source (Target): It should be kept accessible to verify any detail in mapping sheet.
ETL Test Scenarios and Test Cases:
ETL Test Scenario ETL Test Cases Mapping doc validation We will verify the mapping document whether the ETL information provided or not. Log change should maintain in every mapping doc. Validation - We will validate the target and source table structure with the corresponding mapping doc.
- The data type of source and target table should be the same.
- Length of the data type of both source and target should be the same.
- We will verify the data field type, and formats which are specified.
- The length of the source data type should not be less than the length of the target data type.
Constraint Validation The constraint should be defined for a specific table as per our expectation. Data Consistency Issues - Data Type and length of a particular attribute may vary in files or tables through the semantic definition.
- Misuse of integrity constraint.
Completeness Issues - Here, we have to be ensure that all the expected data is loaded into the target table.
- In this scenario, record counts will be compared between source and target.
- We will check the rejected records.
- Data should not be truncated in the column of the truncated table.
- Will check the boundary value analysis.
- We will compare unique values of critical fields between the data loaded in warehouse and source data.
Correctness Issues - This scenario is used to correct the data, which is misspelled or inaccurately recorded.
- To correct the data, that is null, non-unique, and out of range.
Transformation - This scenario is used to check the transformation.
Data Quality - This scenario is used to check the number and validate it.
- Data Check: This scenario will follow the date format, and it should be same for all the records.
- Precision check
- Data check
- Null check
Null Validate - This scenario will verify the null values, where "Not null" values are specified for a specific column.
Duplicate Check - In this scenario, we will check the validation of unique key, primary key, and any other column should be unique as per business requirement having any duplicate rows.
- We will check if any duplicate values exist in any column which is extracted from multiple column sources and combine them into one column.
- As per the client requirements, we need to ensure that there are no duplicates in a combination of multiple columns with target only.
Date Validation - Date values are using many areas in development to know the row creation date.
- Identify the existing records as per the ETL development perspective.
- Sometimes on the date values, the updates and inserts are generated.
Data Cleanness - The unnecessary column should be removed before loading into the staging area.
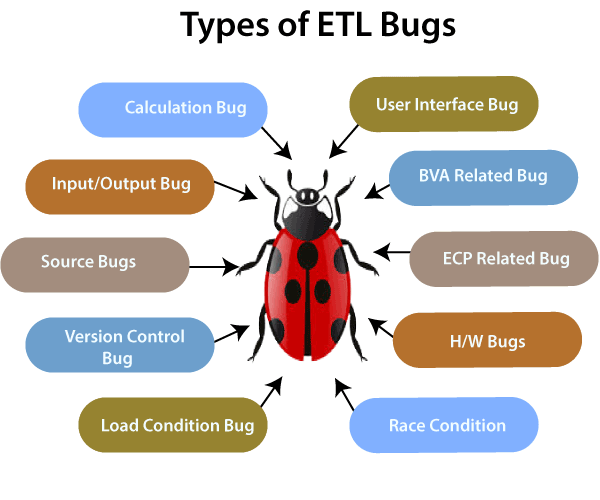
Types of ETL Bugs Description User Interface Bugs These bugs are related to the Graphical User Interface of an application such as, color, font style, navigation, spelling check, etc. Input-Output Bugs In this type of bug, the application starts taking invalid values, and the valid values are rejected. Boundary value analysis bug These bugs check for the minimum and maximum values. Calculation Bugs Calculation bugs show the mathematical errors, and most of the time the final output is wrong. Load Condition Bugs These types of bugs don't allow multiple users. It does not allow the data which is user accepted. Race Condition Bugs In this kind of bugs, the system will not run properly. It starts crashing or hanging. Equivalence Class Partitioning bugs This type of bug results invalid or invalid types. Version Control Bugs These types of bugs usually occur in Regression Testing and do not give any information on versions. Hardware Bugs In this type of bug, the device will not respond to the application as expected. Help Source Bugs This bug will result as the mistakes in the help documents.
- We will validate the target and source table structure with the corresponding mapping doc.
- The data type of source and target table should be the same.
- Length of the data type of both source and target should be the same.
- We will verify the data field type, and formats which are specified.
- The length of the source data type should not be less than the length of the target data type.
- Data Type and length of a particular attribute may vary in files or tables through the semantic definition.
- Misuse of integrity constraint.
- Here, we have to be ensure that all the expected data is loaded into the target table.
- In this scenario, record counts will be compared between source and target.
- We will check the rejected records.
- Data should not be truncated in the column of the truncated table.
- Will check the boundary value analysis.
- We will compare unique values of critical fields between the data loaded in warehouse and source data.
- This scenario is used to correct the data, which is misspelled or inaccurately recorded.
- To correct the data, that is null, non-unique, and out of range.
- This scenario is used to check the transformation.
- This scenario is used to check the number and validate it.
- Data Check: This scenario will follow the date format, and it should be same for all the records.
- Precision check
- Data check
- Null check
- This scenario will verify the null values, where "Not null" values are specified for a specific column.
- In this scenario, we will check the validation of unique key, primary key, and any other column should be unique as per business requirement having any duplicate rows.
- We will check if any duplicate values exist in any column which is extracted from multiple column sources and combine them into one column.
- As per the client requirements, we need to ensure that there are no duplicates in a combination of multiple columns with target only.
- Date values are using many areas in development to know the row creation date.
- Identify the existing records as per the ETL development perspective.
- Sometimes on the date values, the updates and inserts are generated.
- The unnecessary column should be removed before loading into the staging area.
Responsibility of ETL tester
ETL tester is responsible for validating the data sources, applying transformation logic, and loading the data in the target table, extraction of data.
The responsibilities of ETL tester are:
Verify the table in the source system. It involves the following types of operation:
- Count Check
- Data Type check
- Reconcile records with source data
- Ensure no spam data is loaded
- Remove duplicate data
- Check all the keys are in place
Apply Transformation Logic
Transformation logic is applied before loading the data. It involves the following operations:
- Transformation logic is applied before and after checking the record of the count.
- Validation of data flow from the staging area to the intermediate table.
- Check the data threshold validation; for example, the age value should not be more than 100.
- Check the surrogate key
Data Loading
Data is loaded from the staging area to the target systems. It involves the following operations:
We will check if the aggregate values and calculated measures loaded in the fact table.
- During the loading of the data, we will check the modeling views based on the target table.
- We will check, if the CDC has been applied to the incremental load table.
- Check the data dimension table and review the history of the table.
- Check the reports of BI which are based on the loaded fact and dimension table as per the expected results.
Testing of ETL Tools
ETL testers are required to test the test cases and tools as well. It involves the following operations:
- Test the ETL tool and its functions
- Test the ETL Data Warehouse system
- Create, design and execute the test cases and test plan
- Test the flat file data transfer
Advantages of ETL Testing
Benefits of ETL testing are given below:
- ETL testing can extract or receive data from any data sources at the same time.
- ETL can load the data from heterogeneous sources to a single generalized (frequent)\ different target at the same time.
- ETL can be able to load different types of the goal at the same time.
- ETL can be able to extract required business data from various sources and can be needed load business data into the different target as the desired format.
- ETL can perform any data transformation according to the business.
Disadvantages of ETL Testing
Disadvantages of ETL testing are given below:
- One of the main disadvantages of ETL testing is that we must be a data-oriented developer or database analyst to use it.
- When we need a fast response, it is not ideal for real-time or on-demand access.
- ETL testing will take months to put on any place.
- It is challenging to keep the data in the changing requirement.
heading:
ETL testers are required to test the test cases and tools as well. It involves the following operation:
- Test the ETL tool and its function
- Test the ETL Data Warehouse system
- Create, design and execute the test cases and test plan
- Test the flat file data transfer
Database Testing
Computer applications are more complex these days with technologies like Android and also with lots of Smartphone apps. The more complex the front ends, the more intricate the back ends become.
So it is all the more important to learn about DB testing and be able to validate Databases effectively to ensure security and quality databases.
In this tutorial, you will learn all about Data Testing – why, how and what to test?
The Database is one of the inevitable parts of a Software Application.
It does not matter whether it is a web, desktop or mobile, client-server, peer-to-peer, enterprise, or individual business; the Database is required everywhere at the backend.
Similarly, whether it is Healthcare, Finance, Leasing, Retail, Mailing application, or controlling a spaceship; a Database is always in action behind the scene.
As the complexity of application increases, the need for a stronger and secure Database emerges. In the same way, for the applications with a high frequency of transactions (For Example, Banking or Finance application), the necessity of a fully-featured DB Tool is coupled.
Nowadays, we have big data that is large and complex that the traditional databases can’t handle them.
There are several Database tools are available in the market For Example, MS-Access, MS SQL Server, SQL Server, Oracle, Oracle Financial, MySQL, PostgreSQL, DB2, Toad, Admirer, etc. These tools vary in cost, robustness, features, and security. Each of these has its own benefits and drawbacks.
Why Test Database?
Below, we will see why the following aspects of a DB should be validated:
#1) Data Mapping
In software systems, data often travels back and forth from the UI (user interface) to the backend DB and vice versa. So these are some aspects to watch for:
- Check whether the fields in the UI/frontend forms are mapped consistently with the corresponding fields in the DB table. Typically this mapping information is defined in the requirements documents.
- Whenever a certain action is performed at the front end of an application, a corresponding CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update and Delete) action gets invoked at the back end. A tester will have to check if the right action is invoked and whether the invoked action in itself is successful or not.
#2) ACID Properties Validation
Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. Every transaction a DB performs has to adhere to these four properties.
- Atomicity means that a transaction either fails or passes. This means that even if a single part of the transaction fails- it means that the entire transaction has failed. Usually, this is called the “all-or-nothing” rule.
- Consistency: A transaction will always result in a valid state of the DB
- Isolation: If there are multiple transactions and they are executed all at once, the result/state of the DB should be the same as if they were executed one after the other.
- Durability: Once a transaction is done and committed, no external factors like power loss or crash should be able to change it
Suggested reading =>> MySQL Transaction Tutorial
#3) Data Integrity
For any of the CRUD Operations, the updated and most recent values/status of shared data should appear on all the forms and screens. The value should not be updated on one screen and display an older value on another one.
When the application is under execution, the end-user mainly utilizes the ‘CRUD’ operations facilitated by the DB Tool.
C: Create – When user ‘Save’ any new transaction, ‘Create’ operation is performed.
R: Retrieve – When user ‘Search’ or ‘View’ any saved transaction, ‘Retrieve’ operation is performed.
U: Update – When user ‘Edit’ or ‘Modify’ an existing record, the ‘Update’ operation of DB is performed.
D: Delete – When a user ‘Remove’ any record from the system, ‘Delete’ operation of DB is performed.
Any database operation performed by the end-user is always one of the above four.
So devise your DB test cases in a way to include checking the data in all the places it appears to see if it is consistently the same.
#4) Business Rule Conformity
More complexity in Databases means more complicated components like relational constraints, triggers, stored procedures, etc. So testers will have to come up with appropriate SQL queries in order to validate these complex objects.
What To Test (Database Testing Checklist)
#1) Transactions
When testing Transactions it is important to make sure that they satisfy the ACID properties.
These are the statements commonly used:
- BEGIN TRANSACTION TRANSACTION#
- END TRANSACTION TRANSACTION#
The Rollback statement ensures that the database remains in a consistent state.
- ROLLBACK TRANSACTION#
After these statements are executed, use a Select to make sure the changes have been reflected.
- SELECT * FROM TABLENAME <tables which involve the transactions>
#2) Database Schemas
A Database Schema is nothing more than a formal definition of how the data is going to be organized inside a DB. To test it:
- Identify the Requirements based on which the Database operates. Sample Requirements:
- Primary keys to be created before any other fields are created.
- Foreign keys should be completely indexed for easy retrieval and search.
- Field names starting or ending with certain characters.
- Fields with a constraint that certain values can or cannot be inserted.
- Use one of the following methods according to the relevance:
- SQL Query DESC<table name> to validate the schema.
- Regular expressions for validating the names of the individual fields and their values
- Tools like SchemaCrawler
#3) Triggers
When a certain event takes place on a certain table, a piece of code (a trigger) can be auto-instructed to be executed.
For Example, a new student joined a school. The student is taking 2 classes: math and science. The student is added to the “student table”. A Trigger could add the student to the corresponding subject tables once he is added to the student table.
The common method to test is to execute the SQL query embedded in the Trigger independently first and record the result. Follow this up with executing the Trigger as a whole. Compare the results.
These are tested in both the Black-box and White-box testing phases.
- White box testing: Stubs and Drivers are used to insert or update or delete data that would result in the trigger being invoked. The basic idea is to just test the DB alone even before the integration with the front end (UI) is made.
- Black box testing:
a) Since the UI and DB, integration is now available; we can Insert/Delete/Update data from the front end in a way that the Trigger gets invoked. Following that, Select statements can be used to retrieve the DB data to see if the Trigger was successful in performing the intended operation.
b) The second way to test this is to directly load the data that would invoke the Trigger and see if it works as intended.
#4) Stored Procedures
Stored Procedures are more or less similar to user-defined functions. These can be invoked by Call Procedure/Execute Procedure statements and the output is usually in the form of result sets.
These are stored in the RDBMS and are available for applications.
These are also tested during:
- White box testing: Stubs are used to invoke the stored procedures and then the results are validated against the expected values.
- Black box testing: Perform an operation from the front end (UI) of the application and check for the execution of the stored procedure and its results.
#5) Field Constraints
The Default value, Unique value, and Foreign key:
- Perform a front-end operation which exercises the Database object condition
- Validate the results with a SQL Query.
Checking the default value for a certain field is quite simple. It is part of business rule validation. You can do it manually or you can use tools like QTP. Manually, you can perform an action that will add value other than the default value of the field from the front end and see if it results in an error.
The following is a sample VBScript code:
Function VBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation(pattern , string_to_match)Set newregexp = new RegExpnewregexp.Pattern = “&lt;Default value as required by the business requirements&gt;”newregexp.Ignorecase = Truenewregexp.Global = TrueVBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation = newregexp.Test(string_to_match)End FunctionMsgbox VBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation(pattern , string_to_match) |
The result of the above code is True if the default value exists or False if it doesn’t.
Checking the unique value can be done exactly the way we did for the default values. Try entering values from the UI that will violate this rule and see if an error is displayed.
Automation VB Script code can be:
Function VBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation(pattern , string_to_match)Set newregexp = new RegExpnewregexp.Pattern = “&lt;Unique value as required by the business requirements&gt;”newregexp.Ignorecase = Truenewregexp.Global = TrueVBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation = newregexp.Test(string_to_match)End FunctionMsgbox VBScriptRegularexpressionvlaidation(pattern , string_to_match) |
For the Foreign Key constraint validation use data loads that directly input data that violate the constraint and see if the application restricts them or not. Along with the back end data load, perform the front end UI operations too in a way that will violate the constraints and see if the relevant error is displayed.
Data Testing Activities
Database Tester Should Focus on Following Testing Activities:
#1) Ensure Data Mapping:
Data Mapping is one of the key aspects in the database and it should be tested rigorously by every software tester.
Make sure that the mapping between different forms or screens of AUT and its DB is not only accurate but also per the design documents (SRS/BRS) or code. Basically, you need to validate the mapping between every front-end field with its corresponding backend database field.
For all CRUD operations, verify that respective tables and records are updated when the user clicks ‘Save’, ‘Update’, ‘Search’ or ‘Delete’ from GUI of the application.
What you need to verify:
- Table mapping, column mapping, and Data type mapping.
- Lookup Data Mapping.
- Correct CRUD operation is invoked for every user action at UI.
- CRUD operation is successful.
#2) Ensure ACID Properties of Transactions:
ACID properties of DB Transactions refer to the ‘Atomicity’, ‘Consistency’, ‘Isolation’ and ‘Durability’. Proper testing of these four properties must be done during the database test activity. You need to verify that every single transaction satisfies the ACID properties of the database.
Let us take a simple example through below SQL code:
CREATE TABLE acidtest (A INTEGER, B INTEGER, CHECK (A + B = 100));
The ACID test table will have two columns – A & B. There is an integrity constraint that the sum of values in A and B should always be 100.
Atomicity test will ensure any transaction performed on this table is all or none i.e. no records are updated if any step of the transaction is failed.
Consistency test will ensure that whenever the value in column A or B is updated, the sum always remains 100. It won’t allow insertion/deletion/update in A or B if the total sum is anything other than 100.
Isolation test will ensure that if two transactions are happening at the same time and trying to modify the data of the ACID test table, then these tractions are executing in isolation.
Durability test will ensure that once a transaction over this table has been committed, it will remain so, even in the event of power loss, crashes, or errors.
This area demands more rigorous, thorough and keen testing if your application is using the distributed database.
#3) Ensure Data Integrity
Consider that different modules (i.e. screens or forms) of application use the same data in different ways and perform all the CRUD operations on the data.
In that case, make sure that the latest state of data is reflected everywhere. The system must show the updated and most recent values or the status of such shared data on all the forms and screens. This is called as Data Integrity.
Test cases for validating Database Data Integrity:
- Check if all the Triggers are in place to update reference table records.
- Check if any incorrect/invalid data exists in the major columns of each table.
- Try to insert wrong data in tables and observe if any failure occurs.
- Check what happens if you try to insert a child before inserting its parent (try to play with Primary and foreign keys).
- Test if any failure occurs if you delete a record that is still referenced by data in any other table.
- Check if replicated servers and databases are in sync.
#4) Ensure the Accuracy of the implemented Business Rules:
Today, Databases are not meant only to store the records. In fact, Databases have been evolved into extremely powerful tools that provide ample support to the developers to implement the business logic at the DB level.
Some simple examples of powerful features are ‘Referential Integrity’, Relational constraints, Triggers, and stored procedures.
So, using these and many other features offered by DBs, developers implement the business logic at the DB level. The tester must ensure that the implemented business logic is correct and works accurately.
The above points describe the four most important ‘What To’ of testing DB. Now, let’s move on to the ‘How To’ part.
How To Test The Database (Step-By-Step Process)
The general test process testing database is not very different from any other application.
The following are the core steps:
Step #1) Prepare the environment
Step #2) Run a test
Step #3) Check test result
Step #4) Validate according to the expected results
Step #5) Report the findings to the respective stakeholders
Usually, SQL queries are used to develop the tests. The most commonly used command is “Select”.
Select * from <tablename> where <condition>
Apart from Select, SQL has 3 important types of commands:
- DDL: Data definition language
- DML: Data manipulation language
- DCL: Data control language
Let us see the syntax for the most commonly used statements.
Data Definition language Uses CREATE, ALTER, RENAME, DROP and TRUNCATE to handle tables (and indexes).
Data Manipulation language Includes statements to add, update and delete records.
Data control language: Deals with giving authorization to users for manipulation and access to the data. Grant and Revoke are the two statements used.
Grant syntax:
Grant select/update
On <table name>
To <user id1, user id2…useridn>;
Revoke syntax:
Revokeselect/update
on <table name>
from<user id1, user id2…useridn>;
Some Practical Tips
#1) Write Queries yourself:
To test the Database accurately, the tester should have very good knowledge of SQL and DML (Data Manipulation Language) statements. The tester should also know the internal DB structure of AUT.
You can combine GUI and data verification in respective tables for better coverage. If you are using the SQL server then you can make use of SQL Query Analyzer for writing queries, executing them and retrieving results.
This is the best and robust way of testing a database when the application is of a small or medium level of complexity.
If the application is very complex then it may be hard or impossible for the tester to write all the required SQL queries. For complex queries, you take help from the developer. I always recommend this method as it gives you confidence in testing and also enhances your SQL skills.
#2) Observe the data in each table:
You can perform data verification using the results of CRUD operations. This can be done manually by using application UI when you know the database integration. But this can be a tedious and cumbersome task when there is huge data in different database tables.
For Manual Data Testing, the Database tester must possess a good knowledge of database table structure.
#3) Get queries from the developers:
This is the simplest way to test the Database. Perform any CRUD operation from GUI and verify its impacts by executing the respective SQL queries obtained from the developer. It neither requires a good knowledge of SQL nor requires a good knowledge of the application’s DB structure.
But this method needs to be used cautiously. What if the query given by the developer is semantically wrong or does not fulfill the user’s requirement correctly? The process will simply fail to validate data.
#4) Make use of Database Automation Testing tools:
There are several tools available for the Data Testing process. You should choose the correct tool as per your needs and make the best use of it.
Conclusion
With all these features, factors and processes to test on a database, there is an increasing demand for the testers to be technically proficient in the key Database concepts. Despite some of the negative beliefs that testing a database creates new bottlenecks and is a lot of additional expenditure – this is a realm of testing that is attracting significant attention and demand.






Comments
Post a Comment