Manual Testing Course-Day 14
Smoke Testing
Smoke Testing is a software testing process that determines whether the deployed software build is stable or not. Smoke testing is a confirmation for QA team to proceed with further software testing. It consists of a minimal set of tests run on each build to test software functionalities. Smoke testing is also known as "Build Verification Testing" or “Confidence Testing.”
In simple terms, we are verifying whether the important features are working and there are no showstoppers in the build that is under testing.
It is a mini and rapid regression test of major functionality. It is a simple test that shows the product is ready for testing. This helps determine if the build is flawed as to make any further testing a waste of time and resources.
The smoke tests qualify the build for further formal testing. The main aim of smoke testing is to detect early major issues. Smoke tests are designed to demonstrate system stability and conformance to requirements.
A build includes all data files, libraries, reusable modules, engineered components that are required to implement one or more product functions.
When do we do smoke testing
Smoke Testing is done whenever the new functionalities of software are developed and integrated with existing build that is deployed in QA/staging environment. It ensures that all critical functionalities are working correctly or not.
In this testing method, the development team deploys the build in QA. The subsets of test cases are taken, and then testers run test cases on the build. The QA team test the application against the critical functionalities. These series of test cases are designed to expose errors that are in build. If these tests are passed, QA team continues with Functional Testing.
Any failure indicates a need to handle the system back to the development team. Whenever there is a change in the build, we perform Smoke Testing to ensure the stability.
Example: -New registration button is added in the login window and build is deployed with the new code. We perform smoke testing on a new build.
Who will do Smoke Testing
After releasing the build to QA environment, Smoke Testing is performed by QA engineers/QA lead. Whenever there is a new build, QA team determines the major functionality in the application to perform smoke testing. QA team checks for showstoppers in the application that is under testing.
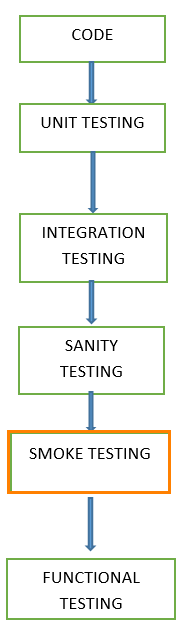
Testing done in a development environment on the code to ensure the correctness of the application before releasing build to QA, this is known as Sanity testing. It is usually narrow and deep testing. It is a process which verifies that the application under development meets its basic functional requirements.
Sanity testing determines the completion of the development phase and makes a decision whether to pass or not to pass software product for further testing phase.
Why do we do smoke testing?
Smoke testing plays an important role in software development as it ensures the correctness of the system in initial stages. By this, we can save test effort. As a result, smoke tests bring the system to a good state. Once we complete smoke testing then only we start functional testing.
- All the show stoppers in the build will get identified by performing smoke testing.
- Smoke testing is done after the build is released to QA. With the help of smoke testing, most of the defects are identified at initial stages of software development.
- With smoke testing, we simplify the detection and correction of major defects.
- By smoke testing, QA team can find defects to the application functionality that may have surfaced by the new code.
- Smoke testing finds the major severity defects.
Example 1: Logging window: Able to move to next window with valid username and password on clicking submit button.
Example 2: User unable to sign out from the webpage.
How to do Smoke Testing ?
Smoke Testing is usually done manually though there is a possibility of accomplishing the same through automation. It may vary from organization to organization.
Manual Smoke testing
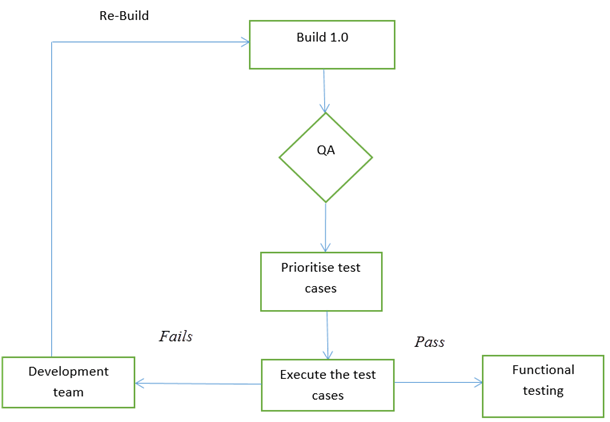
In general, smoke testing is done manually. It approaches varies from one organization to other. Smoke testing is carried to ensure the navigation of critical paths is as expected and doesn't hamper the functionality. Once the build is released to QA, high priority functionality test cases are to be taken and are tested to find the critical defects in the system. If the test passes, we continue the functional testing. If the test fails, the build is rejected and sent back to the development team for correction. QA again starts smoke testing with a new build version. Smoke testing is performed on new build and will get integrated with old builds to maintain the correctness of the system. Before performing smoke testing, QA team should check for correct build versions.
Smoke testing by Automation
Automation Testing is used for Regression Testing. However, we can also use a set of automated test cases to run against Smoke Test. With the help of automation tests, developers can check build immediately, whenever there is a new build ready for deployment.
Instead of having repeated test manually whenever the new software build is deployed, recorded smoke test cases are executed against the build. It verifies whether the major functionalities still operates properly. If the test fails, then they can correct the build and redeploy the build immediately. By this, we can save time and ensure a quality build to the QA environment.
Using an automated tool, test engineer records all manual steps that are performed in the software build.
Smoke testing cycle
Below flow chart shows how Smoke Testing is executed. Once the build is deployed in QA and, smoke tests are passed we proceed for functional testing. If the smoke test fails, we exit testing until the issue in the build is fixed.
Advantages of Smoke testing
Here are few advantages listed for Smoke Testing.
- Easy to perform testing
- Defects will be identified in early stages.
- Improves the quality of the system
- Reduces the risk
- Progress is easier to access.
- Saves test effort and time
- Easy to detect critical errors and correction of errors.
- It runs quickly
- Minimises integration risks
What happens if we don't do Smoke testing
If we don't perform smoke testing in early stages, defects may be encountered in later stages where it can be cost effective. And the Defect found in later stages can be show stoppers where it may affect the release of deliverables.
Sample Smoke Test Cases Example
| T.ID | TEST SCENARIOS | DESCRIPTION | TEST STEP | EXPECTED RESULT | ACTUAL RESULT | STATUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Valid login credentials | Test the login functionality of the web application to ensure that a registered user is allowed to login with username and password | 1.Launch the application 2.Navigate the login page 3.Enter valid username 4.Enter valid password 5.Click on login button | Login should be success | as expected | Pass |
| 2 | Adding item functionality | Able to add item to the cart | 1.Select categories list 2.Add the item to cart | Item should get added to the cart | Item is not getting added to the cart | Fail |
| 3 | Sign out functionality | Check sign out functionality | 1. select sign out button | The user should be able to sign out. | User is not able to sign out | Fail |
Summary:
In Software Engineering, Smoke testing should be performed on each and every build without fail as it helps to find defects in early stages. Smoke test activity is the final step before the software build enters the system stage. Smoke tests must be performed on each build that is turned to testing. This applies to new development and major and minor releases of the system.
Before performing smoke testing, QA team must ensure the correct build version of the application under test. It is a simple process which takes a minimum time to test the stability of the application.
Smoke tests can minimise test effort, and can improve the quality of the application. Smoke testing can be done either manually or by automation depending on the client and the organization.
Sanity Testing Vs Smoke Testing
Smoke and Sanity testing difference is the most misunderstood topic in Software Testing. There is an enormous amount of literature on the subject, but most of them are confusing. The following article makes an attempt to address the confusion.
The key differences between Smoke Testing and Sanity Testing can be learned with the help of the following diagram -
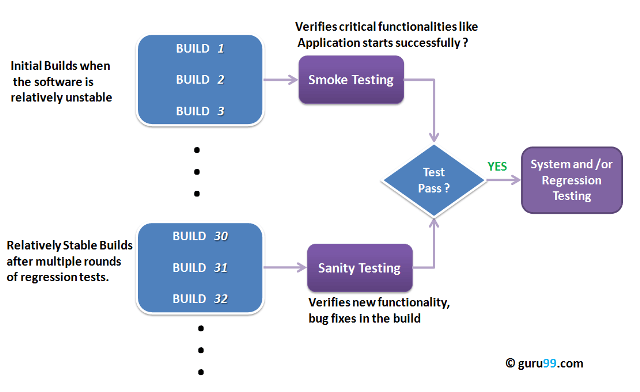
Smoke Testing vs Sanity Testing
To appreciate the above diagram lets first understand -
What is a Software Build?
If you are developing a simple computer program which consists of only one source code file, you merely need to compile and link this one file, to produce an executable file. This process is very simple.
Usually, this is not the case. A typical Software Project consists of hundreds or even thousands of source code files. Creating an executable program from these source files is a complicated and time-consuming task.
You need to use "build" software to create an executable program and the process is called " Software Build"
Smoke Testing
Smoke Testing is a software testing technique performed post software build to verify that the critical functionalities of software are working fine. It is executed before any detailed functional or regression tests are executed. The main purpose of smoke testing is to reject a software application with defects so that QA team does not waste time testing broken software application.
KEY DIFFERENCE
- Smoke Testing has a goal to verify “stability” whereas Sanity Testing has a goal to verify “rationality”.
- Smoke Testing is done by both developers or testers whereas Sanity Testing is done by testers.
- Smoke Testing verifies the critical functionalities of the system whereas Sanity Testing verifies the new functionality like bug fixes.
- Smoke testing is a subset of acceptance testing whereas Sanity testing is a subset of Regression Testing.
- Smoke testing is documented or scripted whereas Sanity testing isn’t.
- Smoke testing verifies the entire system from end to end whereas Sanity Testing verifies only a particular component.
What is Sanity Testing?
Sanity testing is a kind of Software Testing performed after receiving a software build, with minor changes in code, or functionality, to ascertain that the bugs have been fixed and no further issues are introduced due to these changes. The goal is to determine that the proposed functionality works roughly as expected. If sanity test fails, the build is rejected to save the time and costs involved in a more rigorous testing.
The objective is "not" to verify thoroughly the new functionality but to determine that the developer has applied some rationality (sanity) while producing the software. For instance, if your scientific calculator gives the result of 2 + 2 =5! Then, there is no point testing the advanced functionalities like sin 30 + cos 50.
Smoke Testing Vs Sanity Testing - Key Differences
Following is the difference between Sanity and Smoke testing:
| Smoke Testing | Sanity Testing |
|---|---|
| Smoke Testing is performed to ascertain that the critical functionalities of the program is working fine | Sanity Testing is done to check the new functionality/bugs have been fixed |
| The objective of this testing is to verify the "stability" of the system in order to proceed with more rigorous testing | The objective of the testing is to verify the "rationality" of the system in order to proceed with more rigorous testing |
| This testing is performed by the developers or testers | Sanity testing in software testing is usually performed by testers |
| Smoke testing is usually documented or scripted | Sanity testing is usually not documented and is unscripted |
| Smoke testing is a subset of Acceptance testing | Sanity testing is a subset of Regression Testing |
| Smoke testing exercises the entire system from end to end | Sanity testing exercises only the particular component of the entire system |
| Smoke testing is like General Health Check Up | Sanity Testing is like specialized health check up |
Points to note.
- Both Sanity and Smoke testing are ways to avoid wasting time and effort by quickly determining whether an application is too flawed to merit any rigorous testing.
- Smoke Testing is also called tester acceptance testing.
- Smoke testing performed on a particular build is also known as a build verification test.
- One of the best industry practice is to conduct a Daily build and smoke test in software projects.
- Both smoke and sanity tests can be executed manually or using an automation tool. When automated tools are used, the tests are often initiated by the same process that generates the build itself.
- As per the needs of testing, you may have to execute both Sanity and Smoke Tests in the software build. In such cases, you will first execute Smoke tests and then go ahead with Sanity Testing. In industry, test cases for Sanity Testing are commonly combined with that for smoke tests, to speed up test execution. Hence, it's a common that the terms are often confused and used interchangeably
What is Regression Testing?
REGRESSION TESTING is defined as a type of software testing to confirm that a recent program or code change has not adversely affected existing features.
Regression Testing is nothing but a full or partial selection of already executed test cases which are re-executed to ensure existing functionalities work fine.
This testing is done to make sure that new code changes should not have side effects on the existing functionalities. It ensures that the old code still works once the latest code changes are done.
The Need of Regression Testing mainly arises whenever there is requirement to change the code and we need to test whether the modified code affects the other part of software application or not. Moreover, regression testing is needed, when a new feature is added to the software application and for defect fixing as well as performance issue fixing.
In order to do Regression Testing process, we need to first debug the code to identify the bugs. Once the bugs are identified, required changes are made to fix it, then the regression testing is done by selecting relevant test cases from the test suite that covers both modified and affected parts of the code.
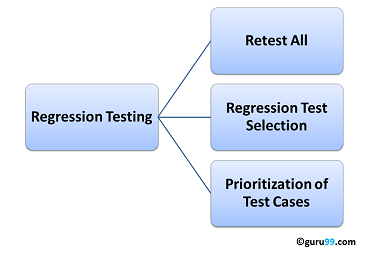
Software maintenance is an activity which includes enhancements, error corrections, optimization and deletion of existing features. These modifications may cause the system to work incorrectly. Therefore, Regression Testing becomes necessary. Regression Testing can be carried out using the following techniques:
Retest All
- This is one of the methods for Regression Testing in which all the tests in the existing test bucket or suite should be re-executed. This is very expensive as it requires huge time and resources.
Regression Test Selection
Regression Test Selection is a technique in which some selected test cases from test suite are executed to test whether the modified code affects the software application or not. Test cases are categorized into two parts, reusable test cases which can be used in further regression cycles and obsolete test cases which can not be used in succeeding cycles.
Prioritization of Test Cases
- Prioritize the test cases depending on business impact, critical & frequently used functionalities. Selection of test cases based on priority will greatly reduce the regression test suite.
Selecting test cases for regression testing
It was found from industry data that a good number of the defects reported by customers were due to last minute bug fixes creating side effects and hence selecting the Test Case for regression testing is an art and not that easy. Effective Regression Tests can be done by selecting the following test cases -
- Test cases which have frequent defects
- Functionalities which are more visible to the users
- Test cases which verify core features of the product
- Test cases of Functionalities which has undergone more and recent changes
- All Integration Test Cases
- All Complex Test Cases
- Boundary value test cases
- A sample of Successful test cases
- A sample of Failure test cases
Regression Testing Tools
If your software undergoes frequent changes, regression testing costs will escalate. In such cases, Manual execution of test cases increases test execution time as well as costs. Automation of regression test cases is the smart choice in such cases. The extent of automation depends on the number of test cases that remain re-usable for successive regression cycles.
Following are the most important tools used for both functional and regression testing in software engineering:
Selenium: This is an open source tool used for automating web applications. Selenium can be used for browser-based regression testing.
Quick Test Professional (QTP): HP Quick Test Professional is automated software designed to automate functional and regression test cases. It uses VBScript language for automation. It is a Data-driven, Keyword based tool.
Rational Functional Tester (RFT): IBM's rational functional tester is a Java tool used to automate the test cases of software applications. This is primarily used for automating regression test cases and it also integrates with Rational Test Manager.
Regression Testing and Configuration Management
Configuration Management during Regression Testing becomes imperative in Agile Environments where a code is being continuously modified. To ensure effective regression tests, observe the following :
- Code being regression tested should be under a configuration management tool
- No changes must be allowed to code, during the regression test phase. Regression test code must be kept immune to developer changes.
- The database used for regression testing must be isolated. No database changes must be allowed
Difference between Re-Testing and Regression Testing:
Retesting means testing the functionality or bug again to ensure the code is fixed. If it is not fixed, Defect needs to be re-opened. If fixed, Defect is closed.
Regression testing means testing your software application when it undergoes a code change to ensure that the new code has not affected other parts of the software.
Challenges in Regression Testing:
Following are the major testing problems for doing regression testing:
- With successive regression runs, test suites become fairly large. Due to time and budget constraints, the entire regression test suite cannot be executed
- Minimizing the test suite while achieving maximum Test coverage remains a challenge
- Determination of frequency of Regression Tests, i.e., after every modification or every build update or after a bunch of bug fixes, is a challenge.
What is the difference between Regression Testing and Retesting?
Regression Testing is a type of software testing executed to ensure whether a code change/update/release/patch has not unfavourably disturbed current features & functions of an application.
Re-testing is a type of testing performed to check whether test cases that were unsuccessful in the final execution are successfully passed after the defects are repaired.
In the Regression Testing, the test cases are extracted from functional testing to ensure that no new defects are included due to the software update/change & to check whether original features and functionality are working as expected. Regression testing also ensures that no new defect is introduced to the system. Once the regression test suite is created, the test cases can be automated using automation tool but the same is not applicable for Re-testing.
Jumping into the detailed comparison
Regression Testing Re-Testing Regression testing is to ensure that changes have not affected unchanged part. Retesting is done to make sure that the tests cases which failed in last execution are passed after the defects are fixed. Regression testing is not carried out for specific defect fixes. Retesting is carried out based on the defect fixes. In Regression testing, the test cases which passed earlier can be included to check the functionality which was working earlier. In Retesting, the cases which are failed earlier can be included to check if the functionality failure in an earlier build. Regression test cases are derived from the functional specification, the user manuals, user tutorials, and defect reports in relation to corrected problems. Test cases for Retesting cannot be prepared before start testing. In Retesting, test cases that are failed in the prior execution are only re-executed. Automation is the key for regression testing. Manual regression testing tends to get more expensive with each new release. Automation always complements the regression test process. Test cases for re-testing cannot be automated due to uncertainty Defect verification doesn’t fall under Regression testing. Defect verification is coming under Retesting. Based on the resource availability the Regression testing can be carried out in parallel with Retesting. Priority of Retesting over Regression testing is higher, so it is carried out before regression testing.
In regression testing, the defect logged by tester while testing the software application is fixed by the developer. In Retesting the same defect is checked to make sure whether the defect is fixed or not using steps to reproduce mentioned in the defect.
Regression Testing is a type of software testing executed to ensure whether a code change/update/release/patch has not unfavourably disturbed current features & functions of an application.
Re-testing is a type of testing performed to check whether test cases that were unsuccessful in the final execution are successfully passed after the defects are repaired.
In the Regression Testing, the test cases are extracted from functional testing to ensure that no new defects are included due to the software update/change & to check whether original features and functionality are working as expected. Regression testing also ensures that no new defect is introduced to the system. Once the regression test suite is created, the test cases can be automated using automation tool but the same is not applicable for Re-testing.
Jumping into the detailed comparison
| Regression Testing | Re-Testing |
| Regression testing is to ensure that changes have not affected unchanged part. | Retesting is done to make sure that the tests cases which failed in last execution are passed after the defects are fixed. |
| Regression testing is not carried out for specific defect fixes. | Retesting is carried out based on the defect fixes. |
| In Regression testing, the test cases which passed earlier can be included to check the functionality which was working earlier. | In Retesting, the cases which are failed earlier can be included to check if the functionality failure in an earlier build. |
| Regression test cases are derived from the functional specification, the user manuals, user tutorials, and defect reports in relation to corrected problems. | Test cases for Retesting cannot be prepared before start testing. In Retesting, test cases that are failed in the prior execution are only re-executed. |
| Automation is the key for regression testing. Manual regression testing tends to get more expensive with each new release. Automation always complements the regression test process. | Test cases for re-testing cannot be automated due to uncertainty |
| Defect verification doesn’t fall under Regression testing. | Defect verification is coming under Retesting. |
| Based on the resource availability the Regression testing can be carried out in parallel with Retesting. | Priority of Retesting over Regression testing is higher, so it is carried out before regression testing. |
In regression testing, the defect logged by tester while testing the software application is fixed by the developer. In Retesting the same defect is checked to make sure whether the defect is fixed or not using steps to reproduce mentioned in the defect.

Comments
Post a Comment