Manual Testing Course-Day 7
Test Case Design
There are many different test case design techniques used to test the functionality and various features of your software. Designing good test cases ensure that every aspect of your software gets tested so that you can find and fix any issues.
A basic example of test case design:
Title: Login to the website or app
Description: User should be able to successfully log in to their account on the website/app
Preconditions: User must already be registered and use their correct login details
Assumptions: They are using a supported device or browser to log in
Test Steps:
- Open website or app
- Enter the username and password in the appropriate fields
- Click “login”
Expected Result: The user should log in successfully.
What are the types of test case design techniques?
The main purpose of test case design techniques is to test the functionalities and features of the software with the help of effective test cases. The test case design techniques are broadly classified into three major categories.
- Specification-Based techniques
- Structure-Based techniques
- Experience-Based techniques
1. Specification-Based or Black-Box techniques
This technique leverages the external description of the software such as technical specifications, design, and client’s requirements to design test cases. The technique enables testers to develop test cases that provide full test coverage. The Specification-based or black box test case design techniques are divided further into 5 categories. These categories are as follows:
Boundary Value Analysis (BVA)
This technique is applied to explore errors at the boundary of the input domain. BVA catches any input errors that might interrupt with the proper functioning of the program.
Equivalence Partitioning (EP)
In Equivalence Partitioning, the test input data is partitioned into a number of classes having an equivalent number of data. The test cases are then designed for each class or partition. This helps to reduce the number of test cases.
Decision Table Testing
In this technique, test cases are designed on the basis of the decision tables that are formulated using different combinations of inputs and their corresponding outputs based on various conditions and scenarios adhering to different business rules.
State Transition Diagrams
In this technique, the software under test is perceived as a system having a finite number of states of different types. The transition from one state to another is guided by a set of rules. The rules define the response to different inputs. This technique can be implemented on the systems which have certain workflows within them.
Use Case Testing
A use case is a description of a particular use of the software by a user. In this technique, the test cases are designed to execute different business scenarios and end-user functionalities. Use case testing helps to identify test cases that cover the entire system.
2. Structure-Based or White-Box techniques
The structure-based or white-box technique design test cases based on the internal structure of the software. This technique exhaustively tests the developed code. Developers who have complete information of the software code, its internal structure, and design help to design the test cases. This technique is further divided into five categories.
Statement Testing & Coverage
This technique involves execution of all the executable statements in the source code at least once. The percentage of the executable statements is calculated as per the given requirement. This is the least preferred metric for checking test coverage.
Decision Testing Coverage
This technique is also known as branch coverage is a testing method in which each one of the possible branches from each decision point is executed at least once to ensure all reachable code is executed. This helps to validate all the branches in the code. This helps to ensure that no branch leads to unexpected behavior of the application.
Condition Testing
Condition testing also is known as Predicate coverage testing, each Boolean expression is predicted as TRUE or FALSE. All the testing outcomes are at least tested once. This type of testing involves 100% coverage of the code. The test cases are designed as such that the condition outcomes are easily executed.
Multiple Condition Testing
The purpose of Multiple condition testing is to test the different combination of conditions to get 100% coverage. To ensure complete coverage, two or more test scripts are required which requires more efforts.
All Path Testing
In this technique, the source code of a program is leveraged to find every executable path. This helps to determine all the faults within a particular code.
3. Experience-Based techniques
These techniques are highly dependent on tester’s experience to understand the most important areas of the software. The outcomes of these techniques are based on the skills, knowledge, and expertise of the people involved. The types of experience-based techniques are as follows:
Error Guessing
In this technique, the testers anticipate errors based on their experience, availability of data and their knowledge of product failure. Error guessing is dependent on the skills, intuition, and experience of the testers.
Exploratory Testing
This technique is used to test the application without any formal documentation. There is minimum time available for testing and maximum for test execution. In exploratory testing, the test design and test execution are performed concurrently.
_____________________________________________________________________________
What is Boundary Testing?
Boundary testing is the process of testing between extreme ends or boundaries between partitions of the input values.
- So these extreme ends like Start- End, Lower- Upper, Maximum-Minimum, Just Inside-Just Outside values are called boundary values and the testing is called "boundary testing".
- The basic idea in normal boundary value testing is to select input variable values at their:
- Minimum
- Just above the minimum
- A nominal value
- Just below the maximum
- Maximum
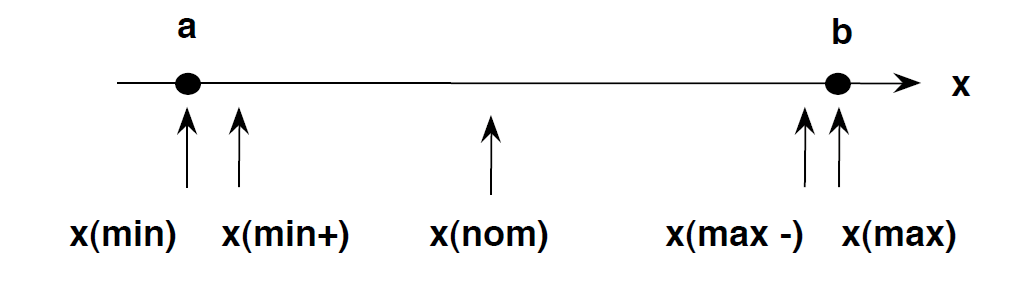
- n Boundary Testing, Equivalence Class Partitioning plays a good role
- Boundary Testing comes after the Equivalence Class Partitioning.
Equivalence Partitioning
Equivalence Partitioning or Equivalence Class Partitioning is type of black box testing technique which can be applied to all levels of software testing like unit, integration, system, etc. In this technique, input data units are divided into equivalent partitions that can be used to derive test cases which reduces time required for testing because of small number of test cases.
- It divides the input data of software into different equivalence data classes.
- You can apply this technique, where there is a range in the input field.
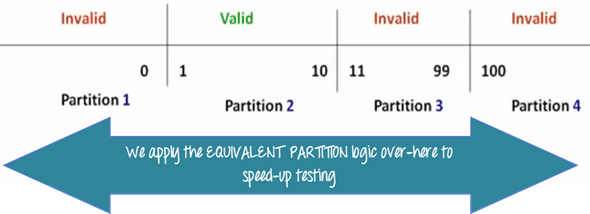
Example 1: Equivalence and Boundary Value
- Let's consider the behavior of Order Pizza Text Box Below
- Pizza values 1 to 10 is considered valid. A success message is shown.
- While value 11 to 99 are considered invalid for order and an error message will appear, "Only 10 Pizza can be ordered"
Here is the test condition
- Any Number greater than 10 entered in the Order Pizza field(let say 11) is considered invalid.
- Any Number less than 1 that is 0 or below, then it is considered invalid.
- Numbers 1 to 10 are considered valid
- Any 3 Digit Number say -100 is invalid.
We cannot test all the possible values because if done, the number of test cases will be more than 100. To address this problem, we use equivalence partitioning hypothesis where we divide the possible values of tickets into groups or sets as shown below where the system behavior can be considered the same.
The divided sets are called Equivalence Partitions or Equivalence Classes. Then we pick only one value from each partition for testing. The hypothesis behind this technique is that if one condition/value in a partition passes all others will also pass. Likewise, if one condition in a partition fails, all other conditions in that partition will fail.
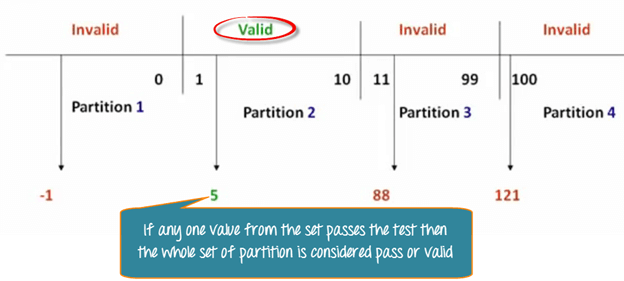
Boundary Value Analysis- in Boundary Value Analysis, you test boundaries between equivalence partitions
In our earlier equivalence partitioning example, instead of checking one value for each partition, you will check the values at the partitions like 0, 1, 10, 11 and so on. As you may observe, you test values at both valid and invalid boundaries. Boundary Value Analysis is also called range checking.
Equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis(BVA) are closely related and can be used together at all levels of testing.
Example 2: Equivalence and Boundary Value
Following password field accepts minimum 6 characters and maximum 10 characters
That means results for values in partitions 0-5, 6-10, 11-14 should be equivalent
| Test Scenario # | Test Scenario Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enter 0 to 5 characters in password field | System should not accept |
| 2 | Enter 6 to 10 characters in password field | System should accept |
| 3 | Enter 11 to 14 character in password field | System should not accept |
Examples 3: Input Box should accept the Number 1 to 10
Here we will see the Boundary Value Test Cases
| Test Scenario Description | Expected Outcome |
| Boundary Value = 0 | System should NOT accept |
| Boundary Value = 1 | System should accept |
| Boundary Value = 2 | System should accept |
| Boundary Value = 9 | System should accept |
| Boundary Value = 10 | System should accept |
| Boundary Value = 11 | System should NOT accept |
Why Equivalence & Boundary Analysis Testing
- This testing is used to reduce a very large number of test cases to manageable chunks.
- Very clear guidelines on determining test cases without compromising on the effectiveness of testing.
- Appropriate for calculation-intensive applications with a large number of variables/inputs
Summary:
- Boundary Analysis testing is used when practically it is impossible to test a large pool of test cases individually
- Two techniques - Boundary value analysis and equivalence partitioning testing techniques are used
- In Equivalence Partitioning, first, you divide a set of test condition into a partition that can be considered.
- In Boundary Value Analysis you then test boundaries between equivalence partitions
- Appropriate for calculation-intensive applications with variables that represent physical quantities
Decision Table Testing: Learn with Example
- Decision Table
A Decision Table is a tabular representation of inputs versus rules/cases/test conditions. It is a very effective tool used for both complex software testing and requirements management. Decision table helps to check all possible combinations of conditions for testing and testers can also identify missed conditions easily. The conditions are indicated as True(T) and False(F) values.
What is Decision Table Testing?
Decision table testing is a software testing technique used to test system behavior for different input combinations. This is a systematic approach where the different input combinations and their corresponding system behavior (Output) are captured in a tabular form. That is why it is also called as a Cause-Effect table where Cause and effects are captured for better test coverage.
Let's learn with an example.
Example 1: How to make Decision Base Table for Login Screen
Let's create a decision table for a login screen.
22.2M202How to write a TEST CASE Software Testing TutorialThe condition is simple if the user provides correct username and password the user will be redirected to the homepage. If any of the input is wrong, an error message will be displayed.Conditions Rule 1 Rule 2 Rule 3 Rule 4 Username (T/F) F T F T Password (T/F) F F T T Output (E/H) E E E H Legend:
- T – Correct username/password
- F – Wrong username/password
- E – Error message is displayed
- H – Home screen is displayed
Interpretation:
- Case 1 – Username and password both were wrong. The user is shown an error message.
- Case 2 – Username was correct, but the password was wrong. The user is shown an error message.
- Case 3 – Username was wrong, but the password was correct. The user is shown an error message.
- Case 4 – Username and password both were correct, and the user navigated to homepage
While converting this to test case, we can create 2 scenarios ,
- Enter correct username and correct password and click on login, and the expected result will be the user should be navigated to homepage
And one from the below scenario
- Enter wrong username and wrong password and click on login, and the expected result will be the user should get an error message
- Enter correct username and wrong password and click on login, and the expected result will be the user should get an error message
- Enter wrong username and correct password and click on login, and the expected result will be the user should get an error message
As they essentially test the same rule.
Example 2: How to make Decision Table for Upload Screen
Now consider a dialogue box which will ask the user to upload photo with certain conditions like –
- You can upload only '.jpg' format image
- file size less than 32kb
- resolution 137*177.
If any of the conditions fails the system will throw corresponding error message stating the issue and if all conditions are met photo will be updated successfully
Let's create the decision table for this case.
Conditions Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 Case 5 Case 6 Case 7 Case 8 Format .jpg .jpg .jpg .jpg Not .jpg Not .jpg Not .jpg Not .jpg Size Less than 32kb Less than 32kb >= 32kb >= 32kb Less than 32kb Less than 32kb >= 32kb >= 32kb resolution 137*177 Not 137*177 137*177 Not 137*177 137*177 Not 137*177 137*177 Not 137*177 Output Photo uploaded Error message resolution mismatch Error message size mismatch Error message size and resolution mismatch Error message for format mismatch Error message format and resolution mismatch Error message for format and size mismatch Error message for format, size, and resolution mismatch For this condition, we can create 8 different test cases and ensure complete coverage based on the above table.
- Upload a photo with format '.jpg', size less than 32kb and resolution 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Photo should upload successfully
- Upload a photo with format '.jpg', size less than 32kb and resolution not 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message resolution mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format '.jpg', size more than 32kb and resolution 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message size mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format '.jpg', size more than equal to 32kb and resolution not 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message size and resolution mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format other than '.jpg', size less than 32kb and resolution 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message for format mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format other than '.jpg', size less than 32kb and resolution not 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message format and resolution mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format other than '.jpg', size more than 32kb and resolution 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message for format and size mismatch should be displayed
- Upload a photo with format other than '.jpg', size more than 32kb and resolution not 137*177 and click on upload. Expected result is Error message for format, size and resolution mismatch should be displayed
Why Decision Table Testing is Important?Decision Table Testing is Important because it helps to test different combinations of conditions and provide better test coverage for complex business logic. When testing the behavior of a large set of inputs where system behaviour differs with each set of input, decision table testing provides good coverage and the representation is simple so it is easy to interpret and use.
In Software Engineering, boundary value and equivalent partition are other similar techniques used to ensure better coverage. They are used if the system shows the same behavior for a large set of inputs. However, in a system where for each set of input values the system behavior is different, boundary value and equivalent partitioning technique are not effective in ensuring good test coverage.
In this case, decision table testing is a good option. This technique can make sure of good coverage, and the representation is simple so that it is easy to interpret and use.
This table can be used as the reference for the requirement and for the functionality development since it is easy to understand and cover all the combinations.
The significance of this technique becomes immediately clear as the number of inputs increases. Number of possible Combinations is given by 2 ^ n , where n is the number of Inputs. For n = 10, which is very common in the web based testing, having big input forms, the number of combinations will be 1024. Obviously, you cannot test all but you will choose a rich sub-set of the possible combinations using decision based testing technique.
Advantages of Decision Table Testing
- When the system behavior is different for different input and not same for a range of inputs, both equivalent partitioning, and boundary value analysis won't help, but decision table can be used.
- The representation is simple so that it can be easily interpreted and is used for development and business as well.
- This table will help to make effective combinations and can ensure a better coverage for testing
- Any complex business conditions can be easily turned into decision tables
- In a case we are going for 100% coverage typically when the input combinations are low, this technique can ensure the coverage.
Disadvantages of Decision Table Testing
The main disadvantage is that when the number of input increases the table will become more complex
_____________________________
What is State Transition Testing?
State Transition Testing is a black box testing technique in which changes made in input conditions cause state changes or output changes in the Application under Test(AUT). State transition testing helps to analyze behaviour of an application for different input conditions. Testers can provide positive and negative input test values and record the system behavior.
It is the model on which the system and the tests are based. Any system where you get a different output for the same input, depending on what has happened before, is a finite state system.
State Transition Testing Technique is helpful where you need to test different system transitions.
When to Use State Transition?
- This can be used when a tester is testing the application for a finite set of input values.
- When the tester is trying to test sequence of events that occur in the application under test. I.e., this will allow the tester to test the application behavior for a sequence of input values.
- When the system under test has a dependency on the events/values in the past.
When to Not Rely On State Transition?
- When the testing is not done for sequential input combinations.
- If the testing is to be done for different functionalities like exploratory testing
Four Parts Of State Transition Diagram
There are 4 main components of the State Transition Model as below
1) States that the software might get
2) Transition from one state to another
3) Events that origin a transition like closing a file or withdrawing money
4) Actions that result from a transition (an error message or being given the cash.)
State Transition Diagram and State Transition Table
There are two main ways to represent or design state transition, State transition diagram, and state transition table.
In state transition diagram the states are shown in boxed texts, and the transition is represented by arrows. It is also called State Chart or Graph. It is useful in identifying valid transitions.
In state transition table all the states are listed on the left side, and the events are described on the top. Each cell in the table represents the state of the system after the event has occurred. It is also called State Table. It is useful in identifying invalid transitions.
How to Make a State Transition (Examples of a State Transition)
Example 1:
Let's consider an ATM system function where if the user enters the invalid password three times the account will be locked.
In this system, if the user enters a valid password in any of the first three attempts the user will be logged in successfully. If the user enters the invalid password in the first or second try, the user will be asked to re-enter the password. And finally, if the user enters incorrect password 3rd time, the account will be blocked.
State transition diagram
In the diagram whenever the user enters the correct PIN he is moved to Access granted state, and if he enters the wrong password he is moved to next try and if he does the same for the 3rd time the account blocked state is reached.
State Transition Table
Correct PIN | Incorrect PIN | |
|---|---|---|
S1) Start | S5 | S2 |
S2) 1st attempt | S5 | S3 |
S3) 2nd attempt | S5 | S4 |
S4) 3rd attempt | S5 | S6 |
S5) Access Granted | - | - |
S6) Account blocked | - | - |
In the table when the user enters the correct PIN, state is transitioned to S5 which is Access granted. And if the user enters a wrong password he is moved to next state. If he does the same 3rd time, he will reach the account blocked state.
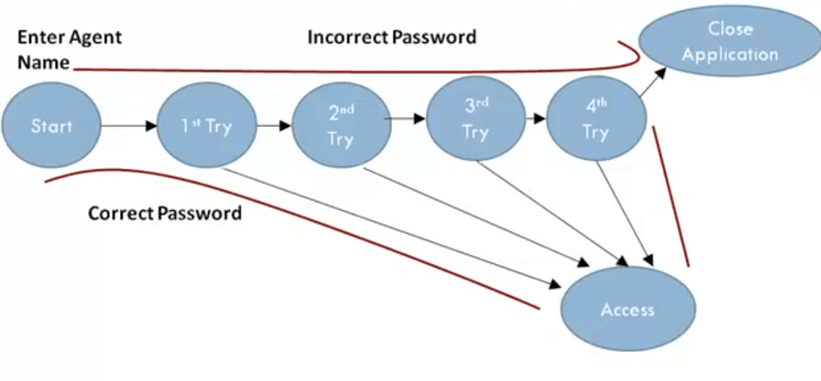
Example 2:
In the flight reservation login screen, consider you have to enter correct agent name and password to access the flight reservation application.
It gives you the access to the application with correct password and login name, but what if you entered the wrong password.
The application allows three attempts, and if users enter the wrong password at 4th attempt, the system closes the application automatically.
The State Graphs helps you determine valid transitions to be tested. In this case, testing with the correct password and with an incorrect password is compulsory. For the test scenarios, log-in on 2nd, 3rd and 4th attempt anyone could be tested.
You can use State Table to determine invalid system transitions.
In a State Table, all the valid states are listed on the left side of the table, and the events that cause them on the top.
Each cell represents the state system will move to when the corresponding event occurs.
For example, while in S1 state you enter a correct password you are taken to state S6 (Access Granted). Suppose if you have entered the wrong password at first attempt you will be taken to state S3 or 2nd Try.
Likewise, you can determine all other states.
Two invalid states are highlighted using this method. Suppose you are in state S6 that is you are already logged into the application, and you open another instance of flight reservation and enter valid or invalid passwords for the same agent. System response for such a scenario needs to be tested.
Advantages and Disadvantages of State Transition Technique
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
This testing technique will provide a pictorial or tabular representation of system behavior which will make the tester to cover and understand the system behavior effectively. | The main disadvantage of this testing technique is that we can't rely in this technique every time. For example, if the system is not a finite system (not in sequential order), this technique cannot be used. |
By using this testing, technique tester can verify that all the conditions are covered, and the results are captured | Another disadvantage is that you have to define all the possible states of a system. While this is all right for small systems, it soon breaks down into larger systems as there is an exponential progression in the number of states. |
Summary:
- State Transition testing is defined as the testing technique in which changes in input conditions cause's state changes in the Application under Test.
- In Software Engineering, State Transition Testing Technique is helpful where you need to test different system transitions.
- Two main ways to represent or design state transition, State transition diagram, and State transition table.
- In state transition diagram the states are shown in boxed texts, and the transition is represented by arrows.
- In state transition table all the states are listed on the left side, and the events are described on the top.
- This main advantage of this testing technique is that it will provide a pictorial or tabular representation of system behavior which will make the tester to cover and understand the system behavior efficiently.
- The main disadvantage of this testing technique is that we can't rely in this technique every time.
______________________________________







Comments
Post a Comment